Behavioral Neuroscience, lecture on Honey Bee and its behavior
Honey Bee Conditioned Drinking
IV. Honey Bee Neuroanatomy
A. Sensory Systems
1. Antennae Lobes (AL)
a. each containing 165 spheroidal neuropil units called glomeruli 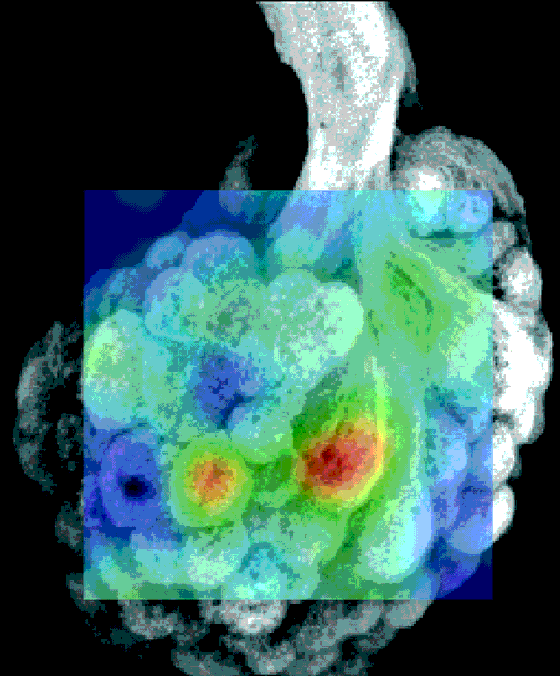 b. local neurons (interneurons) connecting different glomeruli
i. primarily inhibitory
1) mostly g-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic
c. projections neurons
i. relay information to higher-order brain regions
b. local neurons (interneurons) connecting different glomeruli
i. primarily inhibitory
1) mostly g-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic
c. projections neurons
i. relay information to higher-order brain regions 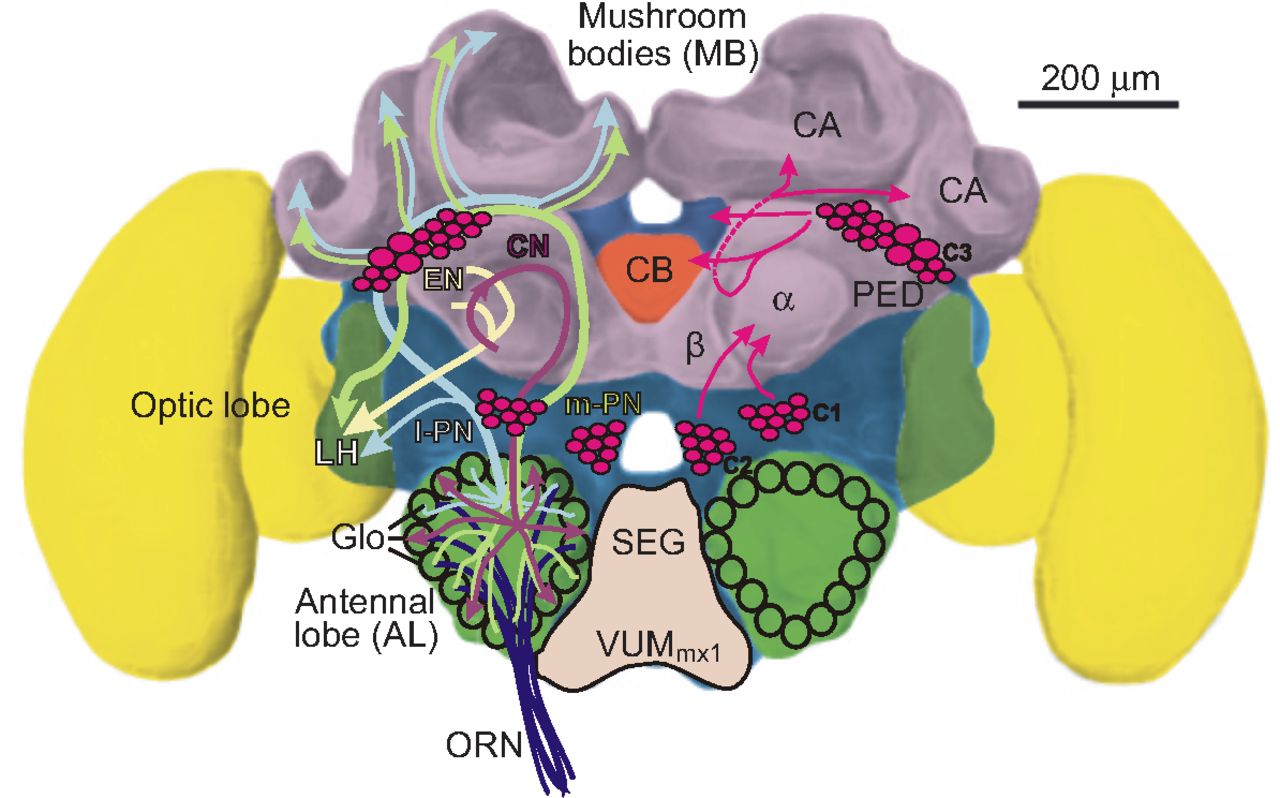 1) lateral horn
2) mushroom bodies
d. First step of synaptic interaction
i. for olfactory receptor neurons and other neuronal types
1) lateral horn
2) mushroom bodies
d. First step of synaptic interaction
i. for olfactory receptor neurons and other neuronal types 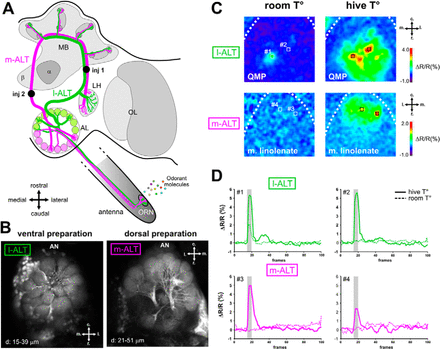 e. mediates olfactory, gustatory, mechanosensory, and auditory information
2. Visual structures (out to in)
a. Eyes
b. Lamellae (L)
c. Medulla (Me)
d. Lobula (Lo)
e. Anterior Optic Tubercle (AOT) major unit (MU)
e. mediates olfactory, gustatory, mechanosensory, and auditory information
2. Visual structures (out to in)
a. Eyes
b. Lamellae (L)
c. Medulla (Me)
d. Lobula (Lo)
e. Anterior Optic Tubercle (AOT) major unit (MU) 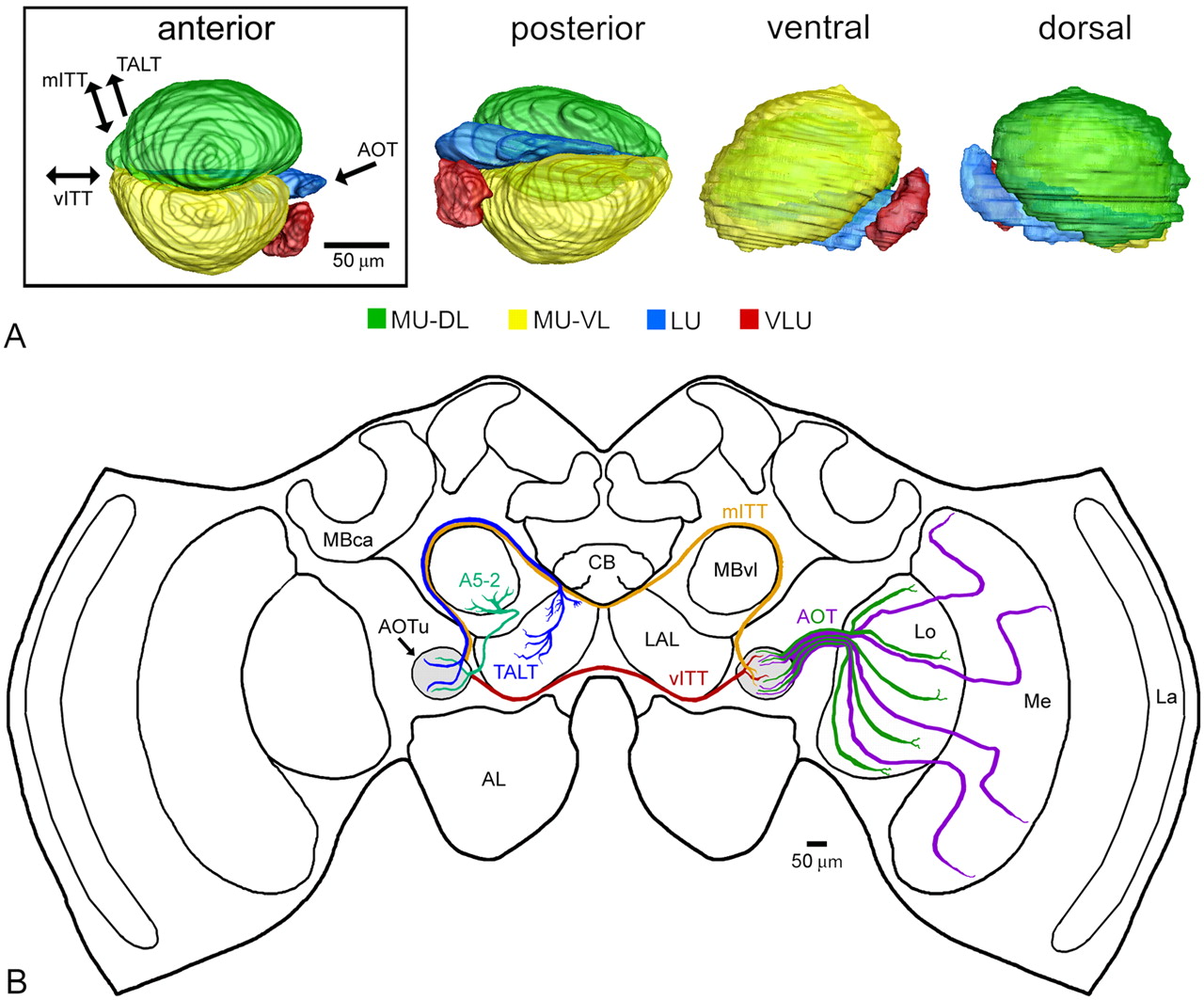 i. dorsal and ventral pathways
1) to mushroom bodies
3. Sensory signals from mouth, proboscis and body
a. Suboesophageal Ganglion (SEG)
i. dorsal and ventral pathways
1) to mushroom bodies
3. Sensory signals from mouth, proboscis and body
a. Suboesophageal Ganglion (SEG) 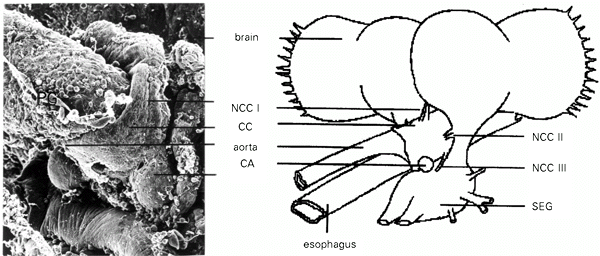 i. receives from and projects to the ventral nerve cord
ii. Contains the Ventral Unpaired Median neurons (VUM)
1) 15 neurons
2) VUM #1 of the maxillary neuromere (VUM-mx1)
i. receives from and projects to the ventral nerve cord
ii. Contains the Ventral Unpaired Median neurons (VUM)
1) 15 neurons
2) VUM #1 of the maxillary neuromere (VUM-mx1) 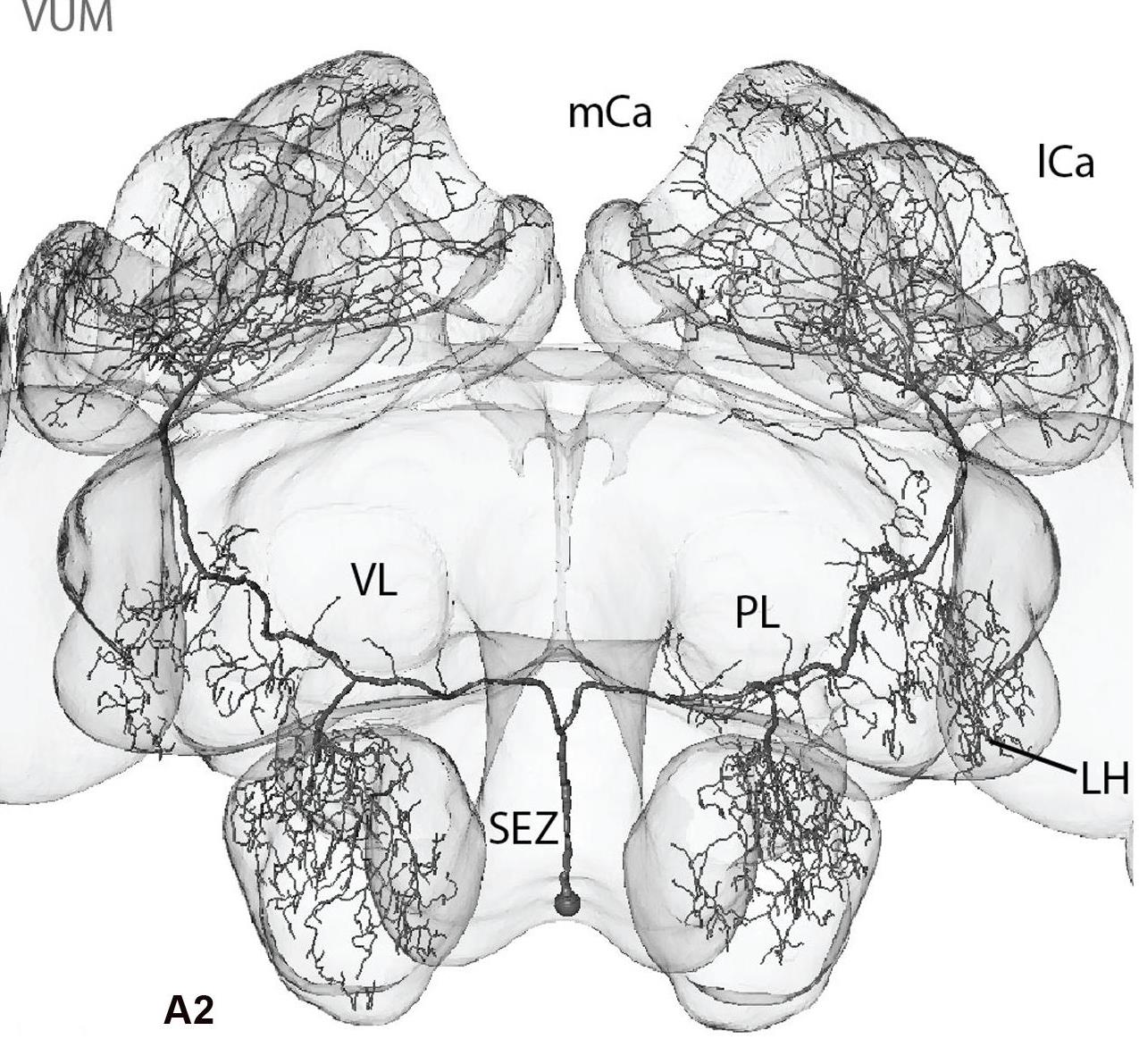 a) transmits gustatory information from sucrose receptors
i) the reward neuron
b) appetitive value system for olfactory learning
c) Octopamine secreting neuron
iii. Interacts with olfactory pathways in anterior lobe, mushroom bodies, and lateral horn
a) transmits gustatory information from sucrose receptors
i) the reward neuron
b) appetitive value system for olfactory learning
c) Octopamine secreting neuron
iii. Interacts with olfactory pathways in anterior lobe, mushroom bodies, and lateral horn
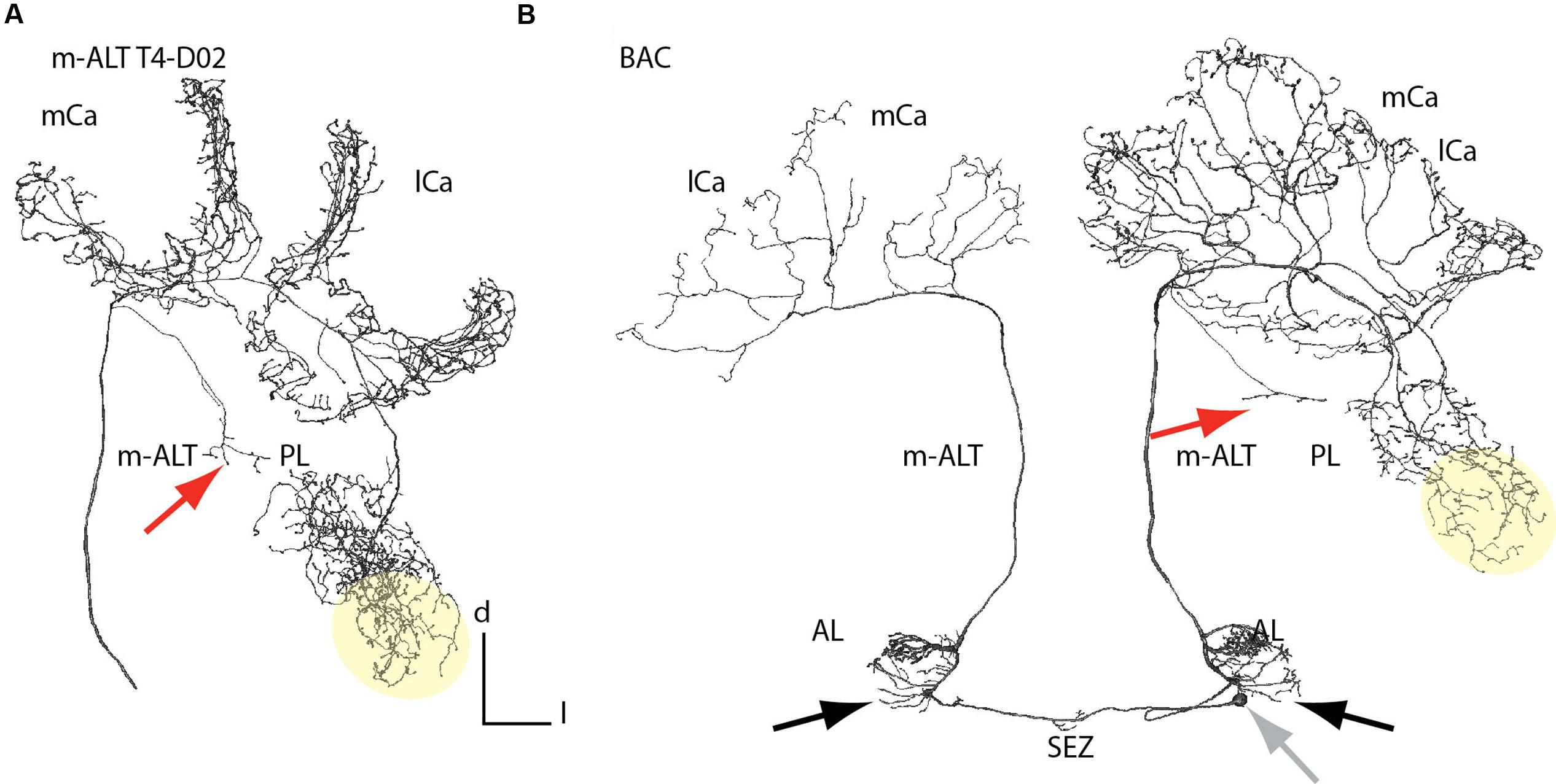 B. Integration and Gating
1. Lateral Horn (LH = lateral protocerebrum)
a. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. pheromone sensitive projection neurons
ii. plant odor sensitive projection neurons
iii. processed separately in two lobes
B. Integration and Gating
1. Lateral Horn (LH = lateral protocerebrum)
a. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. pheromone sensitive projection neurons
ii. plant odor sensitive projection neurons
iii. processed separately in two lobes  1) rewarding vs aversive
2. Mushroom Bodies (MB; top to bottom)
a. medial calyx & lateral calyx
1) rewarding vs aversive
2. Mushroom Bodies (MB; top to bottom)
a. medial calyx & lateral calyx  b. a and b lobes
i. b surrounds a
1) "stalk of mushroom"
c. mediate social behavior and memory
d. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. Involved in olfactory learning and memory
1) Integration of olfactory information with other sensory modalities
e. receives visual projections from the AOT-MU
b. a and b lobes
i. b surrounds a
1) "stalk of mushroom"
c. mediate social behavior and memory
d. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. Involved in olfactory learning and memory
1) Integration of olfactory information with other sensory modalities
e. receives visual projections from the AOT-MU

 b. local neurons (interneurons) connecting different glomeruli
i. primarily inhibitory
1) mostly g-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic
c. projections neurons
i. relay information to higher-order brain regions
b. local neurons (interneurons) connecting different glomeruli
i. primarily inhibitory
1) mostly g-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic
c. projections neurons
i. relay information to higher-order brain regions  1) lateral horn
2) mushroom bodies
d. First step of synaptic interaction
i. for olfactory receptor neurons and other neuronal types
1) lateral horn
2) mushroom bodies
d. First step of synaptic interaction
i. for olfactory receptor neurons and other neuronal types  e. mediates olfactory, gustatory, mechanosensory, and auditory information
2. Visual structures (out to in)
a. Eyes
b. Lamellae (L)
c. Medulla (Me)
d. Lobula (Lo)
e. Anterior Optic Tubercle (AOT) major unit (MU)
e. mediates olfactory, gustatory, mechanosensory, and auditory information
2. Visual structures (out to in)
a. Eyes
b. Lamellae (L)
c. Medulla (Me)
d. Lobula (Lo)
e. Anterior Optic Tubercle (AOT) major unit (MU)  i. dorsal and ventral pathways
1) to mushroom bodies
3. Sensory signals from mouth, proboscis and body
a. Suboesophageal Ganglion (SEG)
i. dorsal and ventral pathways
1) to mushroom bodies
3. Sensory signals from mouth, proboscis and body
a. Suboesophageal Ganglion (SEG)  i. receives from and projects to the ventral nerve cord
ii. Contains the Ventral Unpaired Median neurons (VUM)
1) 15 neurons
2) VUM #1 of the maxillary neuromere (VUM-mx1)
i. receives from and projects to the ventral nerve cord
ii. Contains the Ventral Unpaired Median neurons (VUM)
1) 15 neurons
2) VUM #1 of the maxillary neuromere (VUM-mx1)  a) transmits gustatory information from sucrose receptors
i) the reward neuron
b) appetitive value system for olfactory learning
c) Octopamine secreting neuron
iii. Interacts with olfactory pathways in anterior lobe, mushroom bodies, and lateral horn
a) transmits gustatory information from sucrose receptors
i) the reward neuron
b) appetitive value system for olfactory learning
c) Octopamine secreting neuron
iii. Interacts with olfactory pathways in anterior lobe, mushroom bodies, and lateral horn
 B. Integration and Gating
1. Lateral Horn (LH = lateral protocerebrum)
a. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. pheromone sensitive projection neurons
ii. plant odor sensitive projection neurons
iii. processed separately in two lobes
B. Integration and Gating
1. Lateral Horn (LH = lateral protocerebrum)
a. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. pheromone sensitive projection neurons
ii. plant odor sensitive projection neurons
iii. processed separately in two lobes  b. a and b lobes
i. b surrounds a
1) "stalk of mushroom"
c. mediate social behavior and memory
d. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. Involved in olfactory learning and memory
1) Integration of olfactory information with other sensory modalities
e. receives visual projections from the AOT-MU
b. a and b lobes
i. b surrounds a
1) "stalk of mushroom"
c. mediate social behavior and memory
d. receives projections from neurons in the antenna lobes
i. Involved in olfactory learning and memory
1) Integration of olfactory information with other sensory modalities
e. receives visual projections from the AOT-MU